Creating an SSID Configuration
The Create SSID screen is used to define an SSID configuration and associate an SSID with an Access Point (AP) Group. To access this screen, click on Create SSID on the SSIDs screen.
The Create SSID screen provides the following step-by-step process for creating an SSID configuration:
1. SSID Settings
Basic Information - Configures identifying information for the SSID (for example, profile name, SSID broadcast name, network usage, Captive Portal authentication, and allowed bands).
Authentication Strategy - Selects an authentication server, authentication strategy, and access policy.
Default VLAN/Network - Configures an Access Role Profile for the default network.
Detailed SSID Settings - Configures detailed settings for SSID functionality (for example, hide SSID, advanced security, roaming controls, client controls, and data rates).
2. Network Assignments
Assign SSID(s) to AP Groups - Selects Access Point (AP) Groups from one or more Sites to which the SSID is applied.
3. Schedule and VLAN Mappings
Schedule SSID Availability - Specify the days and/or time during which the SSID is active.
VLAN/Tunnel Mapping - Map the SSID to a VLAN or a Guest Tunnel ID. Client traffic connecting to the Access Point on the SSID network is forwarded on the selected VLAN or Tunnel.
1. SSID Settings
Basic Information
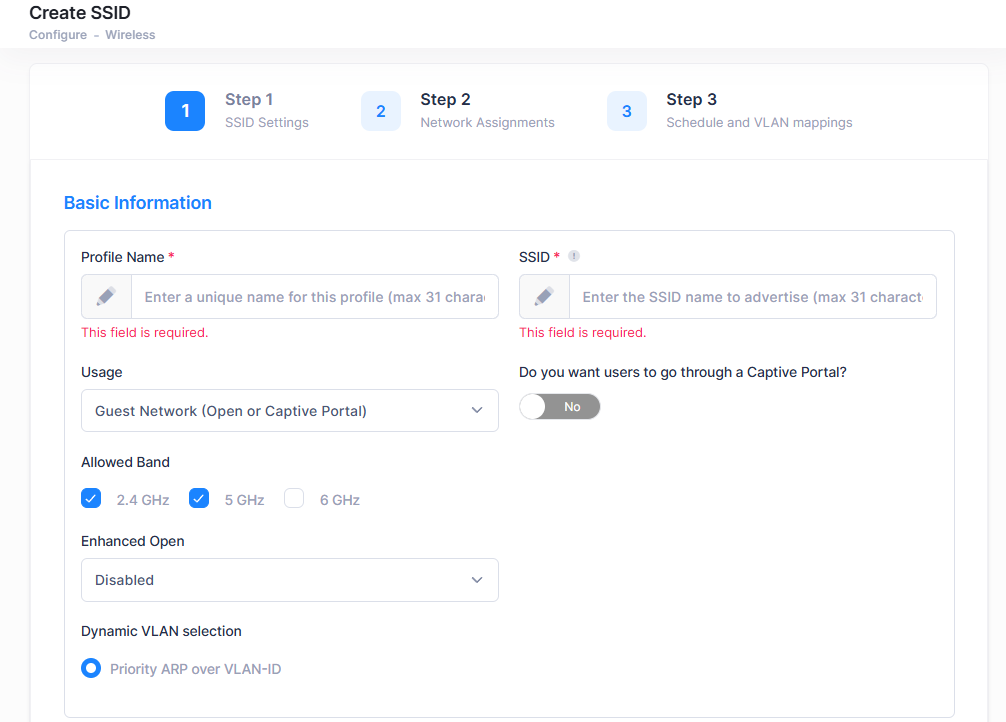
Complete the fields as described below to provide the basic information for the SSID:
Profile Name - A unique name to identify the management profile for the SSID.
SSID - A name that uniquely identifies the wireless network (up to 31 characters). This is the wireless network name that is advertised to wireless clients.
Usage - The SSID network usage. When you select a Usage from the list below, relevant related default configurations such as Access Policy, Authentication Strategy, Guest Access Strategy, and BYOD Access Strategy are automatically created and linked to the SSID using a name derived from the SSID. These configurations can then be customized for your network.
Guest Network (Open or Captive Portal) - Create a network for Guest Users. Suitable for setting up an Open Network with or without a Captive Portal.
Employee BYOD Network - Create a network for employees connecting with their own devices. Suitable for setting up an Open Network for Employee BYOD devices.
Enterprise Network for Employees (802.1X) - Create a network for employees connecting with known devices. Suitable for setting up an Enterprise Network for Employees accessing the network with Company Property or BYOD devices.
Protected Network (Pre-Shared Key & an Optional Captive Portal) - Create a Protected Network for Guest Users. Suitable for setting up a Personal network that requires a PSK/Passphrase, with or without a Captive Portal.
Protected Network for Employees (Pre-Shared Key & BYOD Registration Portal) - Create a Protected Network for employees connecting with their own devices. Suitable for setting up a Personal Network that requires a PSK/Passphrase for employee BYOD devices.
Guest Network (Open or Captive Portal) - Create a network for Guest Users. Suitable for setting up an Open Network with or without a Captive Portal. This is typically used for Guests. When this Usage is selected, configure the following option:
Do you want users to go through a Captive Portal? - Enable/Disable Captive Portal Authentication for the SSID. When enabled, OmniVista Cirrus UPAM Captive Portal is used for authentication.
Enhanced Open - Enables/Disables the use of Wi-Fi Enhanced Open™ to secure an open SSID. Wi-Fi Enhanced Open™ is a security standard that is based on Opportunistic Wireless Encryption (OWE). When enabled, OWE is used to ensure that communication between each pair of endpoints is protected from other endpoints. Data sent between a client and an AP is provided individualized data protection. Wi-Fi Enhanced Open™ offers improved data privacy, while maintaining convenience and ease-of-use. This functionality is particularly useful for provisioning a secure open SSID in public spaces. You can also enable an Enhanced Open Transition Mode for the SSID. When this mode is enabled, the AP broadcasts two different types of BSSID: one legacy Open SSID on 2.4GHz/5.0GHz band and one Enhanced Open SSID on 2.4GHz/5.0GHz/6.0GHz band. This allows both Enhanced Open and Non-Enhanced Open clients to connect to the same open SSID without adversely impacting the end user experience. Select one of the following options to configure the Enhanced Open status for the SSID:
Disabled - Disable Enhanced Open for the SSID. If 2.4GHz and/or 5.0GHz is the allowed band (not 6.0GHz), Enhanced Open is disabled by default. Note that you cannot disable Enhanced Open if the 6.0GHz band is selected.
Enabled - Enable Enhanced Open for the SSID. If 6.0GHz is the allowed band, Enhanced Open is automatically enabled whether 2.4GHz or 5.0GHz is selected.
Enabled - Transition Mode - Enable Enhanced Open Transition Mode for the SSID. Note that the Enhanced Open Transition Mode is supported only on APs running AWOS 4.0.8 or above. Enabling this mode for APs running older AWOS versions may cause the SSID to revert to an open SSID after a reboot. Upgrading your network is highly recommended.
Dynamic VLAN Selection - Determines if an ARP or VLAN ID assignment is given priority.
Priority ARP over VLAN-ID - Enabled by default only if MAC authentication is not selected for the SSID usage. If an AP receives a RADIUS response with ARP and VLAN ID, it will select the ARP.
Priority VLAN-ID over ARP - If MAC authentication is selected for the SSID usage, then priority is given to selecting the VLAN ID over the ARP.
Employee BYOD Network - Create a network for employees connecting with their own devices. Suitable for setting up an Open Network for Employee BYOD devices. Access to the network is granted after BYOD portal authentication.
Enable BYOD Registration - BYOD authentication for the SSID is enabled by default.
Enhanced Open - Enables/Disables the use of Wi-Fi Enhanced Open™ to secure an open SSID. Wi-Fi Enhanced Open™ is a security standard that is based on Opportunistic Wireless Encryption (OWE). When enabled, OWE is used to ensure that communication between each pair of endpoints is protected from other endpoints. Data sent between a client and an AP is provided individualized data protection. Wi-Fi Enhanced Open™ offers improved data privacy, while maintaining convenience and ease-of-use. This functionality is particularly useful for provisioning a secure open SSID in public spaces. You can also enable an Enhanced Open Transition Mode for the SSID. When this mode is enabled, the AP broadcasts two different types of BSSID: one legacy Open SSID on 2.4GHz/5.0GHz band and one Enhanced Open SSID on 2.4GHz/5.0GHz/6.0GHz band. This allows both Enhanced Open and Non-Enhanced Open clients to connect to the same open SSID without adversely impacting the end user experience. Select one of the following options to configure the Enhanced Open status for the SSID:
Disabled - Disable Enhanced Open for the SSID. If 2.4GHz and/or 5.0GHz is the allowed band (not 6.0GHz), Enhanced Open is disabled by default. Note that you cannot disable Enhanced Open if the 6.0GHz band is selected.
Enabled - Enable Enhanced Open for the SSID. If 6.0GHz is the allowed band, Enhanced Open is automatically enabled whether 2.4GHz or 5.0GHz is selected.
Enabled - Transition Mode - Enable Enhanced Open Transition Mode for the SSID. Note that the Enhanced Open Transition Mode is supported only on APs running AWOS 4.0.8 or above. Enabling this mode for APs running older AWOS versions may cause the SSID to revert to an open SSID after a reboot. Upgrading your network is highly recommended.
Dynamic VLAN Selection - Determines if an ARP or VLAN ID assignment is given priority.
Priority ARP over VLAN-ID - Enabled by default. If an AP receives a RADIUS response with ARP and VLAN ID, it will select the ARP.
Priority VLAN-ID over ARP - This option is not supported for Captive Portal or BYOD registration.
Enterprise Network for Employees (802.1X) - Create a network for employees connecting with known devices. Suitable for setting up an Enterprise Network for Employees accessing the network with Company Property or BYOD devices. When this Usage is selected, configure the following options:
Enable BYOD Registration - Enable/Disable BYOD authentication for the SSID.
Encryption Type - Select the encryption type to use from the drop-down menu.
DYNAMIC_WEP - WEP with dynamic keys.
WPA_TKIP - WPA with TKIP encryption and dynamic keys using 802.1X.
WPA_AES - WPA with AES encryption and dynamic keys using 802.1X.
WPA2_TKIP - WPA2 with TKIP encryption and dynamic keys using 802.1X.
WPA2_AES - WPA2 with AES encryption and dynamic keys using 802.1X.
AUTO_WPA_WPA2 - Automatic WPA and WPA2 or mixed mode encryption with dynamic keys using 802.1X.
WPA3_AES256 - WPA3 with CNSA (Suite B) using 802.1X. Note that when WPA3_AES256 encryption is applied to an AP that does not support it, the encryption will automatically fall back to WPA2_AES.
WPA3_AES - WPA3 with AES encryption and dynamic keys using 802.1X.
WPA3-AES Transition Mode - Allows defining a single SSID across the three bands: 2.4GHz, 5GHz, and 6GHz. When selected, Protected Frame Management is automatically set to “Required” for the SSID.
Note: The WPA3_AES Transition Mode is supported only on APs running AWOS 5.0.3 MR or above. Enabling this mode for APs running older AWOS versions may cause the SSID to revert to an open SSID after a reboot. Upgrading your network is highly recommended.
802.1X Bypass - Enable/Disable 802.1X bypass administrative status. When 802.1X bypass is enabled, the user's 802.1X authentication method is performed conditionally based on the result of MAC Authentication. (Default = Disabled).
MAC Authentication - When 802.1X Bypass is enabled, MAC Authentication is automatically enabled and cannot be disabled.
MAC Allow EAP - When 802.1X Bypass is enabled, select Pass or Fail for MAC Allow Extensible Authentication Protocol (EAP).
Dynamic VLAN Selection - Determines if an ARP or VLAN ID assignment is given priority.
Priority ARP over VLAN-ID - If an AP receives a RADIUS response with ARP and VLAN ID, it will select the ARP.
Priority VLAN-ID over ARP - If an AP receives a RADIUS response with ARP and VLAN ID, it will select the VLAN. Note that this option is not supported if BYOD Registration is enabled for the SSID usage.
Protected Network (Pre-Shared Key & an Optional Captive Portal) - Create a Protected Network for Guest Users. Suitable for setting up a Personal network that requires a PSK/Passphrase, with or without a Captive Portal. This is typically used for Guests. When this Usage is selected, configure the following options:
Do you want users to go through a Captive Portal? - Enable/Disable Captive Portal Authentication for the SSID. When enabled, OmniVista Cirrus UPAM Captive Portal is used for authentication.
Encryption Type - Select the encryption type to use from the drop-down menu.
STATIC_WEP - Authentication with Static Wired Equivalent Privacy security algorithm.
WPA_PSK_TKIP - WPA with TKIP encryption using a preshared key.
WPA_PSK_AES - WPA with AES encryption using a preshared key.
WPA_PSK_AES_TKIP - WPA with TKIP and AES mixed encryption using a preshared key.
WPA2_PSK_TKIP - WPA2 with TKIP encryption using a preshared key.
WPA2_PSK_AES - WPA2 with AES encryption using a preshared key.
WPA3_SAE_AES - WPA3 with AES encryption using a preshared key, which ONLY allows WPA3 capable client accessing. When this encryption type is selected, the PSK, Device Specific PSK, and Private Group PSK parameters are not available.
WPA3_PSK_SAE_AES - WPA3 and WPA2 mixed mode, which allow both WPA3 capable client as well as ONLY WPA2 capable client accessing.
AUTO_WPA_WPA2 - Automatic WPA and WPA2 encryption or mixed mode using a preshared key.
Backward Compatibility - Enables/disables using WPA3_PSK_SAE_AES encryption on 2.4GHz and 5.0GHz bands when encryption is automatically set to WPA3_SAE_AES for the 6.0GHz band. When the 6.0GHz band is selected for the SSID, the other bands inherit using WPA3_SAE_AES encryption, which some legacy devices cannot use to connect to the SSID. By default, Backward Compatibility is disabled. When enabled, the WPA3_PSK_SAE_AES Encryption Type is automatically used for the 2.4GHz and 5.0GHz bands and the 6.0GHz band continues to use WPA3_SAE_AES.
Note: If the MLO Band setting includes 6.0GHz, then the Backward Compatibility option is automatically disabled.Key Format - PSK format. Select Passphrase (8-63 characters) or Pre-shared Key (64 characters).
PSK/Passphrase - Enter a PSK Passphrase for authentication.
Confirm PSK/Passphrase - Re-enter the PSK Passphrase.
Device Specific PSK - Enables/Disables Device Specific PSK. Device Specific PSK provides more security than traditional PSK. Select one of the following settings to enable Device Specific PSK.
Prefer Device Specific PSK - If the AAA Server sends the "AES-CBC-128" attribute along with the Radius Access Accept response, this value will be used. If the AAA server does NOT send the "AES-CBC-128" attribute, the key configured in the SSID will be used. Note that when this setting is selected or Device Specific PSK is disabled, the Private Group PSK feature is available to create private groups of client devices based on a Private Group PSK (PPSK) Entry.
Force Device Specific PSK - The value of "AES-CBC-128" attribute returned by AAA Server will be always used, whether it exists or not. The Private Group PSK feature is not available.
Private Group PSK - Enables/Disables the grouping of Device Specific PSKs. (This option is only available when Device Specific PSK is disabled or set to “Prefer Device Specific PSK”.) When Private Group PSK is enabled, complete the following fields to create a PPSK Entry:
PPSK Entries - At least one Private Group PSK (PPSK) Entry is required with the following parameters:
Name - Enter a unique name to identify the PPSK Entry. No two Entries can have the same Name.
Passphrase - Enter a unique PSK Passphrase for authentication. No two Entries can have the same Passphrase.
Access Role Profile - Select the name of an existing Access Role Profile or click on Create Access Role Profile to create a new profile to use (see the Access Role Profile online help). To edit the selected Access Role Profile, click on Edit.
Add more entries - Click for each PPSK Entry that you want to add. Note that each SSID can have up to 16 PPSK Entries. The total number of entries across all SSIDs that exist on an AP cannot exceed 64 on any AP.
Dynamic Private Group PSK - Enables/Disables the dynamic grouping of Device Specific PSKs. (This option is only available when Device Specific PSK is set to “Prefer Device Specific PSK” or “Force Device Specific PSK” and Encryption Type is set to “WPA2_PSK_AES.) When enabled:
The grouping of Device Specific PSKs is processed through UPAM.
The SSID Encryption Type is automatically set to “WPA2_PSK_AES” and Captive Portal is set to no. Both fields are disabled and cannot be changed.
Dynamic Private Group PSK (PGPSK) profiles containing PSK entries are configured in the UPAM database through the Dynamic PGPSK Configuration screen, instead of the SSID screen. Note that you must first create the SSID before you create any Dynamic Private Group PSK profiles.
When a client attempts to authenticate through the SSID, UPAM checks the Company Property list first to see if there’s a match for the device; if not, the list of entries in the Private Group PSK UPAM database are checked. When a device is authenticated through Dynamic Private Group PSK, the matched entry is added to the Dynamic PGPSK Configuration MAC table.
Consider the following scenarios for using Dynamic Private Group PSK to connect to the SSID:
If the client MAC address was added in Company Property with Device Specific PSK disabled, then the client enters the Dynamic Group PSK passphrase to connect to the SSID.
If the client MAC address is not in Company Property, then the client enters the Dynamic Private Group PSK passphrase to connect to the SSID.
If the client MAC address was added in Company Property with Device Specific PSK enabled, then the client cannot connect to the SSID with the Dynamic Private Group PSK passphrase. Instead, the client can use the Device Specific PSK passphrase to connect to an SSID with ARP in MAC Authentication.
Client can only connect to the SSID with one Dynamic Private Group PSK passphrase. For example, if the client enters Dynamic Private Group PSK passphrase “guest-1” and successfully connects to the SSID (MAC address is added to Dynamic Private Group MAC list), but later attempts to connect to an SSID with a different passphrase (such as “guest-2”), the client cannot connect to the SSID. A different passphrase indicates a different role for network access. Each group should have a unique passphrase.
Dynamic VLAN Selection - Determines if an ARP or VLAN ID assignment is given priority.
Priority ARP over VLAN-ID - Enabled by default. If an ARP receives a RADIUS response with ARP and VLAN ID, it will select the ARP.
Priority VLAN-ID over ARP - This option is not supported for Captive Portal or BYOD registration.
Protected Network for Employees (Pre-Shared Key & BYOD Registration Portal) - Create Protected Network for employees connecting with their own devices. Suitable for setting up a Personal Network that requires a PSK/Passphrase for employee BYOD devices. Access to the network is granted after BYOD portal authentication. When this Usage is selected, configure the following options:
Enable BYOD Registration - BYOD authentication for the SSID is enabled by default.
Encryption Type - Select the encryption type to use from the drop-down menu.
STATIC_WEP - Authentication with Static Wired Equivalent Privacy security algorithm.
WPA_PSK_TKIP - WPA with TKIP encryption using a preshared key.
WPA_PSK_AES - WPA with AES encryption using a preshared key.
WPA_PSK_AES_TKIP - WPA with TKIP and AES mixed encryption using a preshared key.
WPA2_PSK_TKIP - WPA2 with TKIP encryption using a preshared key.
WPA2_PSK_AES - WPA2 with AES encryption using a preshared key.
WPA3_SAE_AES - WPA3 with AES encryption using a preshared key, which ONLY allow WPA3 capable client accessing. When this encryption type is selected, the PSK, Device Specific PSK, and Private Group PSK parameters are not available.
WPA3_PSK_SAE_AES - WPA3 and WPA2 mixed mode, which allow both WPA3 capable client as well as ONLY WPA2 capable client accessing.
AUTO_WPA_WPA2 - Automatic WPA and WPA2 encryption or mixed mode using a preshared key.
Backward Compatibility - Enables/disables using WPA3_PSK_SAE_AES encryption on 2.4GHz and 5.0GHz bands when encryption is automatically set to WPA3_SAE_AES for the 6.0GHz band. When the 6.0GHz band is selected for the SSID, the other bands inherit using WPA3_SAE_AES encryption, which some legacy devices cannot use to connect to the SSID. By default, Backward Compatibility is disabled. When enabled, the WPA3_PSK_SAE_AES Encryption Type is automatically used for the 2.4GHz and 5.0GHz bands and the 6.0GHz band continues to use WPA3_SAE_AES.
Note: If the MLO Band setting includes 6.0GHz, then the Backward Compatibility option is automatically disabled.Key Format - PSK format. Select Passphrase (8-63 characters) or Pre-shared Key (64 characters).
PSK/Passphrase - Enter a PSK Passphrase for authentication.
Confirm PSK/Passphrase - Re-enter the PSK Passphrase.
Device Specific PSK - Enables/Disables Device Specific PSK. Device Specific PSK provides more security than traditional PSK. Select one of the following settings to enable Device Specific PSK.
Prefer Device Specific PSK - If the AAA Server sends the "AES-CBC-128" attribute along with the Radius Access Accept response, this value will be used. If the AAA server does NOT send the "AES-CBC-128" attribute, the key configured in the SSID will be used. Note that when this setting is selected or Device Specific PSK is disabled, the Private Group PSK feature is available to create private groups of client devices based on a Private Group PSK (PPSK) Entry.
Force Device Specific PSK - The value of "AES-CBC-128" attribute returned by AAA Server will be always used, whether it exists or not. The Private Group PSK feature is not available.
Private Group PSK - Enables/Disables the grouping of Device Specific PSKs. (Note that this option is only available when Device Specific PSK is disabled or set to “Prefer Device Specific PSK”.) When Private Group PSK is enabled, complete the following fields to create a PPSK Entry:
PPSK Entries - At least one Private Group PSK (PPSK) Entry is required with the following parameters:
Name - Enter a unique name to identify the PPSK Entry. No two Entries can have the same Name.
Passphrase - Enter a unique PSK Passphrase for authentication. No two Entries can have the same Passphrase.
Access Role Profile - Select the name of an existing Access Role Profile or click on Create Access Role Profile to create a new profile to use (see the Access Role Profile online help). To edit the selected Access Role Profile, click on Edit.
Click on Add more entries for each PPSK Entry that you want to create. Note that each SSID can have up to 16 PPSK Entries. The total number of entries across all SSIDs that exist on an AP cannot exceed 64 on any AP..
Dynamic VLAN Selection - Determines if an ARP or VLAN ID assignment is given priority.
Priority ARP over VLAN-ID - Enabled by default. If an AP receives a RADIUS response with ARP and VLAN ID, it will select the ARP.
Priority VLAN-ID over ARP - This option is not supported for Captive Portal or BYOD registration.
Allowed Band - Select one or more of the following band(s) that will be available on the network. Note that when 6 GHz is selected for the Allowed Band of a Protected Network or Protected Network for Employees, the only encryption type supported is WPA3_SAE_AES (which does not support PSK options).
2.4 GHz
5 GHz
6 GHz
Device Specific PSK (DSPSK)
When the Protected Network or the Protected Network for Employees option is selected for the SSID network usage and a device is configured for Device Specific PSK, when the AAA Server sends the RADIUS Access-Accept for MAC Authentication for the device, it will also send the specific pre-shared key for that device, differentiated by the device's MAC Address. This means that each device will have a different key.
Device Specific PSK will only work with a UPAM RADIUS Server and does not support AUTO_WPA_WPA2 encryption. Devices are configured for Device Specific PSK on the Company Property Screen. See the Company Property online help for more information. You can also configure a device for Device Specific PSK from the Authentication Records List. See the Authentication Records online help for more information.
Private Group PSK
When a PSK-enabled SSID is created, you can either create a static PSK or enforce Device Specific PSK. This provides a common Passphrase key, which is suitable for networks requiring network-wide common PSK. Enabling Private Group PSK (PPSK) allows you to create private groups of client devices based on a PPSK Entry. Each client device specifies a Passphrase when connecting to an SSID. If the passphrase matches any of the PPSK Entry, the client is placed in the specified Access Role Profile.
Configuring the Private Group PSK attribute is offered only when Device Specific PSK is Disabled or set to "Prefer Device Specific PSK". When the Device Specific PSK is set to "Force Device Specific PSK", OmniVista will not display the Private Group PSK attribute because the Passphrase specified in Company Property is used instead.
Authentication Strategy
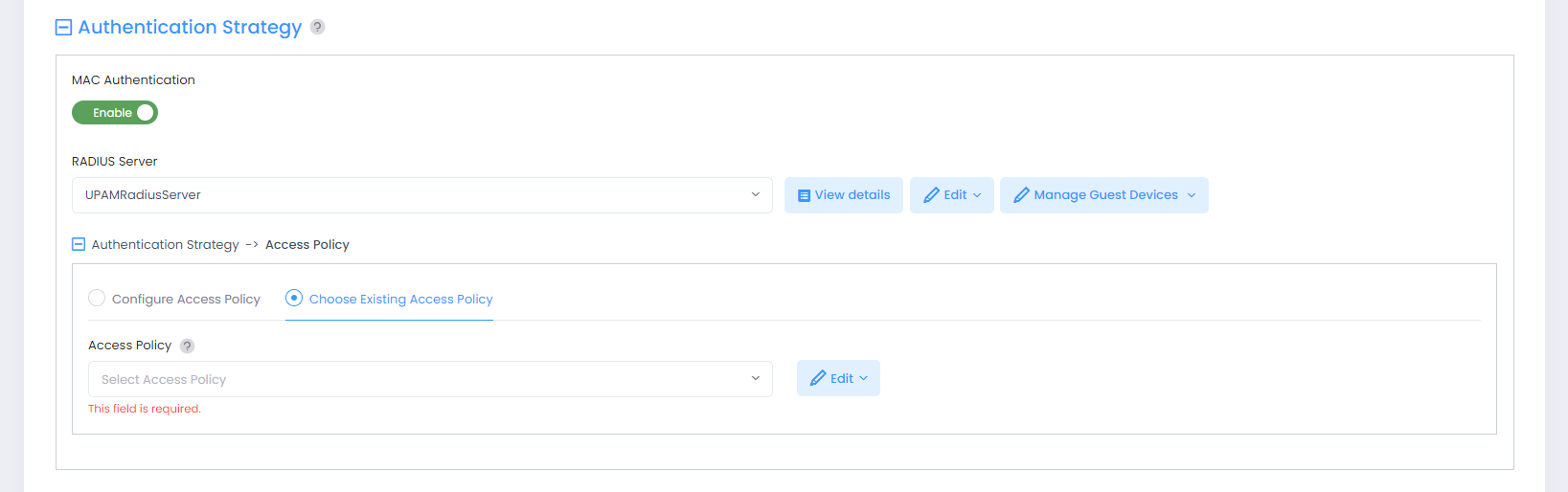
Enable or disable MAC Authentication. When enabled, additional fields are displayed to select the RADIUS Server and the Access Policy to use for the Authentication Strategy. Complete the fields as described below:
RADIUS Server - Select the RADIUS Server to use from the drop-down menu. Note that if you select a RadSec (TLS-Enabled Radius) Server, an AP can only support one RadSec Server and cannot support MAC authentication or External Captive Portal. If there are multiple RadSec Servers set up, make sure that all SSIDs within an AP Group are configured to use the same RadSec server. The following options are available for the selected server:
View details - Display configuration details about the selected RADIUS Server.
Edit - Open the Edit RADIUS Server screen to modify server settings.
Manage Guest Devices - Configure user access to company devices owned by the Organization (for example, printers, IP phones, laptops, tablets). This field may not be available based on the network usage selected for the SSID or the RADIUS Server selected.
Note that when you click on Edit or Manage Guest Devices, you are prompted to either discard current changes to open the related screen or open the related screen in a new browser tab.
Authentication Strategy → Access Policy - Select one of the following options to specify an Access Policy for the SSID Authentication Strategy:
Choose Existing Access Policy (Default) - Select an existing Access Policy from the drop-down menu. The following options are available for the selected policy:
View Details - Display configuration details about the selected Access Policy.
Edit - Open the Edit Access Policy screen to modify the selected Access Policy configuration.
Configure Access Policy - Create a new Access Policy. When you select this option, the Access Policy name is automatically generated by adding “_ _” to the beginning of the SSID name (for example, if the SSID name is “MAC Auth”, then the name assigned to the Access Policy is “_ _MAC Auth”). You can then customize the policy settings, as needed.
Save this as a distinct Access Policy, for reuse - Select this option if you want the automatically created Access Policy to be available for use after the associated SSID has been deleted.
The Access Policy that you create or select defines the Authentication Strategy that UPAM applies when a client connects to the SSID. However, the Access Policy displayed for the SSID configuration is not always the policy used for authentication when the client is connecting to the SSID. This can occur if there are multiple Access Policies with the same precedence and overlapping rules configured through the Access Policies screen (Configure > Network Access > UPAM-NAC > Access Policies).
When a client connects to the SSID, UPAM selects the Access Policy with the highest precedence and evaluates whether its mapping rules align with the client’s connection request. If a match is found, the associated authentication strategy is applied. If two Access Policies with the same precedence have identical mapping rules, UPAM defaults to the policy created first. This behavior may lead to unexpected results.
To prevent ambiguity, ensure that:
a) There are no Access Policies with overlapping rules, or
b) Access Policies with overlapping rules have different precedence. You can adjust the policy precedence configured for the Access Policies (Configure > Network Access > UPAM-NAC > Access Policies) to address these issues.
Default VLAN/Network
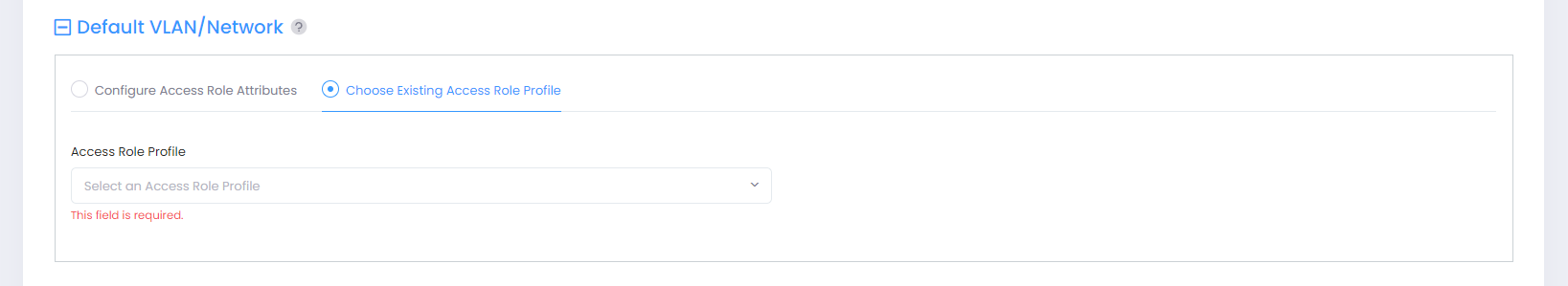
In this section, you can select one of the following options to apply an Access Role Profile to clients joining this SSID, if a role cannot be assigned by other role assignment methods.
Choose Existing Access Role Profile (Default) - Select an existing Access Role Profile from the drop-down menu. The “VLAN” and “Use Tunnel” mappings are set according to the attributes defined in the selected Access Role Profile.
Configure Access Role Attributes - When you select this option, the Access Role Profile name is automatically generated by adding “_ _” to the beginning of the SSID name (for example, if the SSID name is “MAC Auth”, then the name assigned to the Access Role Profile is “_ _MAC Auth”). You can then customize the default profile settings, as needed. See the Creating an Access Role Profile online help for information about configuring profile settings.
Save this as a distinct Access Role Profile, for reuse - Select this option if you want the automatically created Access Role Profile to be available for use after the associated SSID has been deleted.
Detailed SSID Settings
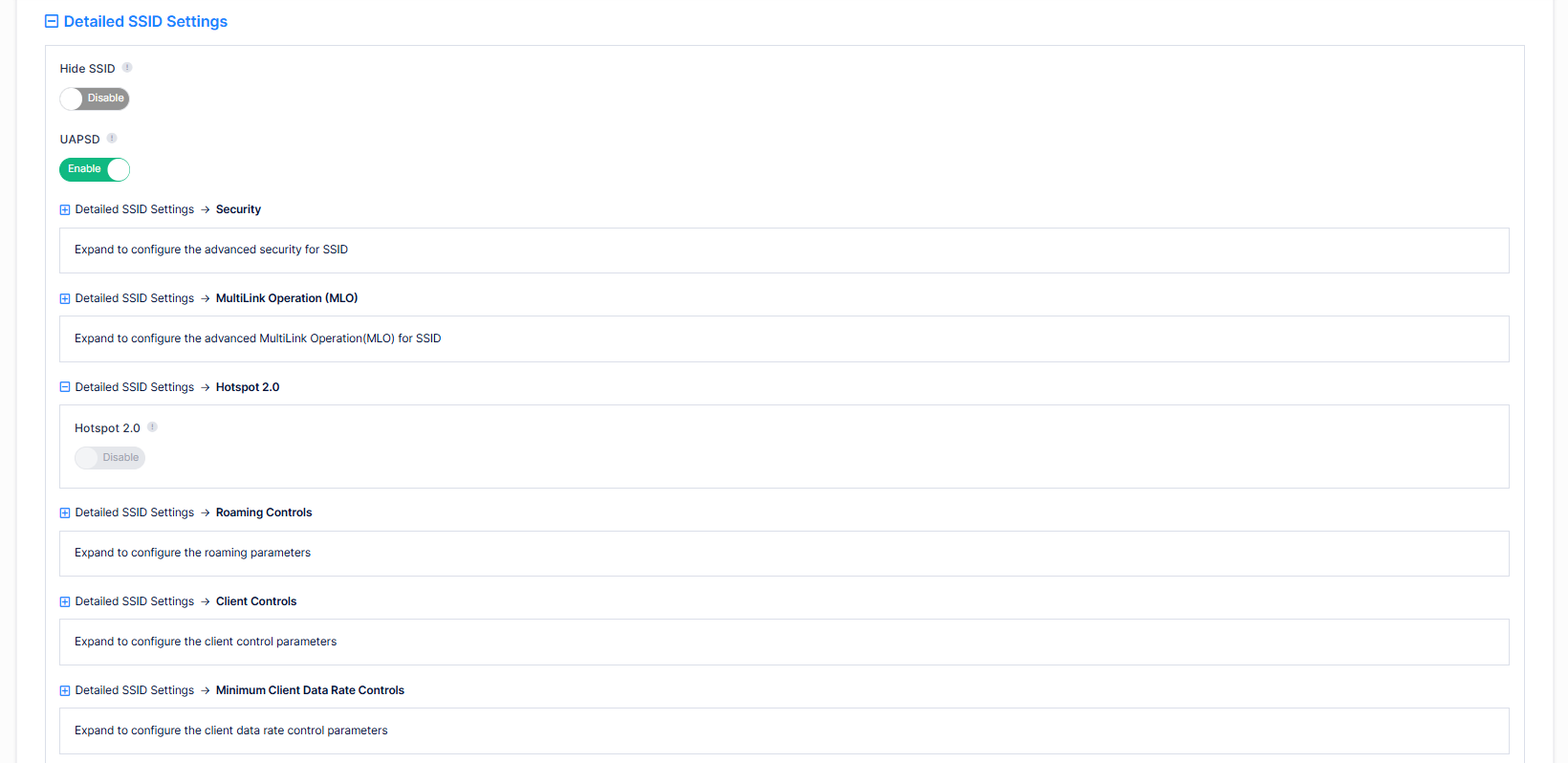
In this section, you can configure advanced SSID settings as described below:
Hide SSID - Enables/Disables SSID in beacon frames. Note that hiding the SSID does very little to increase security. (Default = Disabled)
UAPSD - Enables/Disables Unscheduled Automatic Power Save Delivery (UAPSD) on the SSID. UAPSD is a QoS facility defined in IEEE 802.11e that extends the battery life of mobile clients. In addition to extending battery life, this feature reduces the latency of traffic flow that is delivered over the wireless media. Because UAPSD does not require the client to poll each individual packet that is buffered at the access point, it allows delivery of multiple downlink packets by sending a single uplink trigger packet. (Default = Enabled)
Detailed SSID Settings → Security
Classification Status - Enables/Disables classification. If classification is enabled, traffic will be classified to a role based on the configured classification rules. Note that the precedence of role assignment methods is important. Classification Rules are only used if 802.1X/MAC authentication does not return a role, or the returned role is not matched with any configured roles in the device.
MAC Pass Alt - If MAC Authentication is enabled, select an Access Role Profile to assign to clients that pass MAC Authentication but did not receive a valid Access Role Profile.
Client Isolation - Enables/Disables Client Isolation. If enabled, traffic between clients on the same AP in the SSID is blocked; client traffic can only go toward the router. (Default = Disabled)
Protected Management Frame - Configures whether connections are accepted from clients supporting Protected Management Frame for certain Security Levels/Encryption Types (Enterprise - WPA2_AES, WPA3_AES256, WPA3_AES; Protected- WPA2_PSK_AES, WPA3_SAE_AES, WPA3_PSK_SAE_AES). The Encryption Type option is provided based on the selected Usage for the SSID (see Basic Information above).
Disabled - Disables Protected Management Frame requirements.
Optional - Allows connections from clients supporting Protected Management Frame and clients that do not.
Required - Only allows connections from clients supporting Protected Management Frame.
Detailed SSID Settings → MultiLink Operation (MLO)
MLO - Enables/Disables MLO. (Default = Disabled). Allows for the simultaneous sending and receiving of data between different frequency bands and channels.
MLO Band - When MLO is enabled, the bands selected are taken from the Allowed Band setting. For example, if Allowed Band is set to 2.4GHz and 5GHz, then the MLO band is set to 2.4GHz and 5GHz by default when MLO is enabled. When the Allowed Band is set to 2.4GHz, 5GHz, and 6GHz, you can change the MLO bands as needed. Note that when you change the MLO bands, it does not change the Allowed Bands.
Detailed SSID Settings → Hotspot 2.0
Hotspot 2.0 - Enables/Disables Hotspot 2.0. Hotspot 2.0 is a new standard for public-access Wi-Fi that enables seamless roaming among Wi-Fi networks and between Wi-Fi and cellular networks. Hotspot 2.0 was developed by the Wi-Fi Alliance and the Wireless Broadband Association to enable seamless hand-off of traffic without requiring additional user sign-on and authentication. Note that Hotspot 2.0 is only supported with Enterprise WPA2_AES or Enterprise WPA3_AES256 Encryption. You must first select one of these Encryption types before you can enable Hotspot 2.0.
Operator Name - The operator providing the Hotspot service (0 - 252 characters).
Venue Name - The venue where the Hotspot is hosted (0 - 252 characters).
Venue Type - The type of venue hosting the Hotspot.
Network Detail - The type of Hotspot network.
Domain List - The list of Hotspot Domains. You can have up to 16 Domain Names (1 - 255 characters each).
Roaming OIs - The Roaming Organization Identifier. You can have up to 16 OIs. Each OI field is 3 characters in length if the organizationally unique identifier is an OUI, or 5 octets in length if the organizationally unique identifier is an OUI-36.
Detailed SSID Settings → Roaming Controls
L3 Roaming - Enables/Disables Layer 3 roaming. Layer 3 roaming allows client to move between Access Points and connect to a new IP subnet and VLAN.
FBD Update on Association - Enables/Disables FDB Update on Association. If enabled, when a client roams to a new AP, the AP will send ARP packets to the uplink switch to notify the switch to change the downstream forwarding port for the wireless client's traffic.
802.11k Status - Enables/Disables 802.11k. The 802.11k protocol enables APs and clients to dynamically measure the available radio resources. When 802.11k is enabled, APs and clients send neighbor reports, beacon reports, and link measurement reports to each other.
802.11v Status - Enables/Disables 802.11v. 802.11v standard defines mechanisms for wireless network management enhancements and BSS transition management. It allows client devices to exchange information about the network topology and RF environment. The BSS transition management mechanism enables an Instant AP to request a voice client to transition to a specific AP, or suggest a set of preferred APs to a client due to network load balancing or BSS termination. It also helps the client identify the best AP to transition to as they roam.
Detailed SSID Settings → Client Controls
Max Number of Clients Per Band - The maximum number of clients allowed in each band. (Range = 1 - 256, Default = 64)
802.11b Support - Enables/Disables allowing 11b legacy clients connect to APs.
802.11a/g Support - Enables/Disables allowing 11a/g legacy clients connect to APs.
Detailed SSID Settings → Minimum Client Date Rate Controls
2.4GHz Minimum Client Data Rate Controller - Enables/Disables 2.4G band access control based on client data rate.
2.4GHz Minimum Client Data Rate - 2.4G band client with lower data speed will not be given access.
5GHz Minimum Client Data Rate Controller - Enables/Disables 5G band access control based on client data rate.
5GHz Minimum Client Data Rate - 5G band client with lower data speed will not be given access.
6GHz Minimum Client Data Rate Controller - Enables/Disables 6G band access control based on client data rate.
6GHz Minimum Client Data Rate - 6G band client with lower data speed will not be given access,.
Notes:
Disabling lower bands has an impact on the coverage area.
Depending on the environment, we recommend 12 Mbps or 24 Mbps setting for minimum client data rates.
Higher Mbps value means less coverage; lower value means larger coverage.
Detailed SSID Settings → Minimum MGMT Rate Controls
2.4GHz Minimum MGMT Rate Controller - Enables/Disables 2.4G band wireless management frame rate control.
2.4GHz Minimum MGMT Rate - 2.4G band wireless management frame transmit rate. Higher value means less coverage; lower value means larger coverage.
5GHz Minimum MGMT Rate Controller - Enables/Disables 5G band wireless management frame rate control.
5GHz Minimum MGMT Rate - 5G band wireless management frame transmit rate. Higher value means less coverage; lower value means larger coverage.
6GHz Minimum MGMT Rate Controller - Enables/Disables 6G band wireless management frame rate control.
6GHz Minimum MGMT Rate - 6G band wireless management frame transmit rate. Higher value means less coverage; lower value means larger coverage.
Notes:
Disabling lower bands has an impact on the coverage area.
Depending on the environment, using a 12 Mbps or 24 Mbps setting is recommended for minimum client data rates.
Higher Mbps value means less coverage; lower value means larger coverage.
Detailed SSID Settings → High-Throughput Control
A-MSDU - Enables/Disables Aggregate MAC Service Data Unit. A-MSDU is a structure containing multiple MSDUs, transported within a single (unfragmented) data MAC MPDU.
A-MPDU - Enables/Disables Aggregate MAC Protocol Data Unit. A-MPDU is a method of frame aggregation, where several MPDUs are combined into a single frame for transmission.
Detailed SSID Settings → Power Save Controls
DTIM Interval - The Delivery Traffic Indication Message (DTIM) period in beacons. The DTIM interval determines how often the AP should deliver the buffered broadcast and multicast frames to associated clients in the "power save" mode. The default value is 1, which means the client checks for buffered data on the OAW-IAP at every beacon. You can configure a higher DTIM value for power saving (Range = 1 - 255).
Detailed SSID Settings → 802.11 Frame Controls
Advertise AP Name - Enables/Disables the advertising of the AP name in the standard 802.11 beacon frame with a vendor-specific tag. The default value of Advertise AP name is false. When enabled, the AP name is displayed instead of the AP MAC address.
Detailed SSID Settings → Bandwidth Contract
Upstream Bandwidth - The maximum bandwidth for traffic from the switch to the client
Downstream Bandwidth - The maximum bandwidth for traffic from the client to the switch.
Upstream Burst - The maximum bucket size used for traffic from the switch to the client. The bucket size determines how much the traffic can burst over the maximum bandwidth rate
Downstream Burst -The maximum bucket size used for traffic from the client to the switch. The bucket size determines how much the traffic can burst over the maximum bandwidth rate.
Detailed SSID Settings → Broadcast/Multicast Optimization
Broadcast Key Rotation - Enables/Disables the broadcast key rotation function. If enabled, the broadcast key will be rotated after every interval time.
Broadcast Key Rotation Time Interval - The interval, in minutes, to rotate the broadcast key (Range = 1 - 1440, Default = 15).
Broadcast Filter All - Enables/Disables broadcast filtering. If enabled, all broadcast frames are dropped, except DHCP and Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) frames.
Broadcast Filter ARP - Enables/Disables broadcast filtering for ARP. If enabled, the AP will act as an "ARP Proxy". If the ARP-request packet requests a client's MAC address and the AP knows the client's MAC and IP address, the AP will respond to the ARP-request but not forward the ARP-request (broadcast) to all broadcast domains. This reduces ARP broadcast packet forwarding and significantly improves network performance. Note that APs do not act as ARP proxy for Gratuitous ARP packets. When the station gets an IP from DHCP or IP release/ renew, the station will send Gratuitous ARP packets. AP will not respond to such special ARP packets and broadcast them normally.
Multicast Optimization - Enable/Disables multicast traffic rate optimization.
Multicast Based Channel Utilization - Configures based channel utilization optimization percentage. (Range = 0 - 100, Default = 90)
Number of Clients - Configure the threshold for multicast optimization. This is the maximum number of high-throughput.
Detailed SSID Settings → 802.1p Mapping - Used to configure the uplink and downlink mapping mechanism between Wi-Fi Multimedia (WMM) Access Categories and 802.1p priority. Uplink traffic can only be mapped to a single value. Downlink traffic can be mapped to multiple values. Fields are populated with the default values. To modify a default uplink value, enter a new value in the field. To modify a default downlink value, enter a new value and click on the Add icon. To remove a value, click on the "x" next to the value.
Background - WMM Background will be mapped to the 802.1p value.
Uplink - Maps uplink traffic (from AP to network). (Range = 0 - 7, Default = 1)
Downlink - Maps downlink traffic (from network to AP). (Range = (Range = 0 - 7, Default = 1, 2)
Best Effort - WMM Best Effort will be mapped to the 802.1p value.
Uplink - Maps uplink traffic (from AP to network). (Range = 0 - 7, Default = 0)
Downlink - Maps downlink traffic (from network to AP). (Range = (Range = 0 - 7, Default = 0, 3)
Video - WMM Video will be mapped to the 802.1p value.
Uplink - Maps uplink traffic (from AP to network). (Range = 0 - 7, Default = 4)
Downlink - Maps downlink traffic (from network to AP). (Range = (Range = 0 - 7, Default = 4, 5)
Voice - WMM Voice will be mapped to the 802.1p value.
Uplink - Maps uplink traffic (from AP to network). (Range = 0 - 7, Default = 6)
Downlink - Maps downlink traffic (from network to AP). (Range = (Range = 0 - 7, Default = 6, 7)
Detailed SSID Settings → DSCP Mapping - Used to configure the uplink and downlink mapping mechanism between Wi-Fi Multimedia (WMM) Access Categories and DSCP priority. Uplink traffic can only be mapped to a single value. Downlink traffic can be mapped to multiple values. Fields are populated with the default values. To modify a default uplink value, enter a new value in the field. To modify a default downlink value, enter a new value and click on the Add icon. To remove a value, click on the "x" next to the value.
Trust Original DSCP - If enabled, the original DSCP mapping for uplink traffic is trusted (Default = Disabled).
Background - WMM Background will be mapped to the 802.1p value.
Uplink - Maps uplink traffic (from AP to network). (Range = 0 - 7, Default = 10)
Downlink - Maps downlink traffic (from network to AP). (Range = (Range = 0 - 7, Default = 2, 10)
Best Effort - WMM Best Effort will be mapped to the 802.1p value.
Uplink - Maps uplink traffic (from AP to network). (Range = 0 - 7, Default = 0)
Downlink - Maps downlink traffic (from network to AP). (Range = (Range = 0 - 7, Default = 0, 18)
Video - WMM Video will be mapped to the 802.1p value.
Uplink - Maps uplink traffic (from AP to network). (Range = 0 - 7, Default = 40)
Downlink - Maps downlink traffic (from network to AP). (Range = (Range = 0 - 7, Default = 24, 36, 40)
Voice - WMM Voice will be mapped to the 802.1p value.
Uplink - Maps uplink traffic (from AP to network). (Range = 0 - 7, Default = 46)
Downlink - Maps downlink traffic (from network to AP). (Range = (Range = 0 - 7, Default = 46, 48, 56)
After completing the necessary field values for the SSID Settings tab, click on Next to go to the Network Assignments tab (Step 2).
2. Network Assignments
An SSID configuration is applied to an AP Group; all APs belonging to the assigned group will use the same SSID configuration. The Network Assignments tab of the Create SSID screen is where you can apply SSIDs to AP Groups, as shown here:
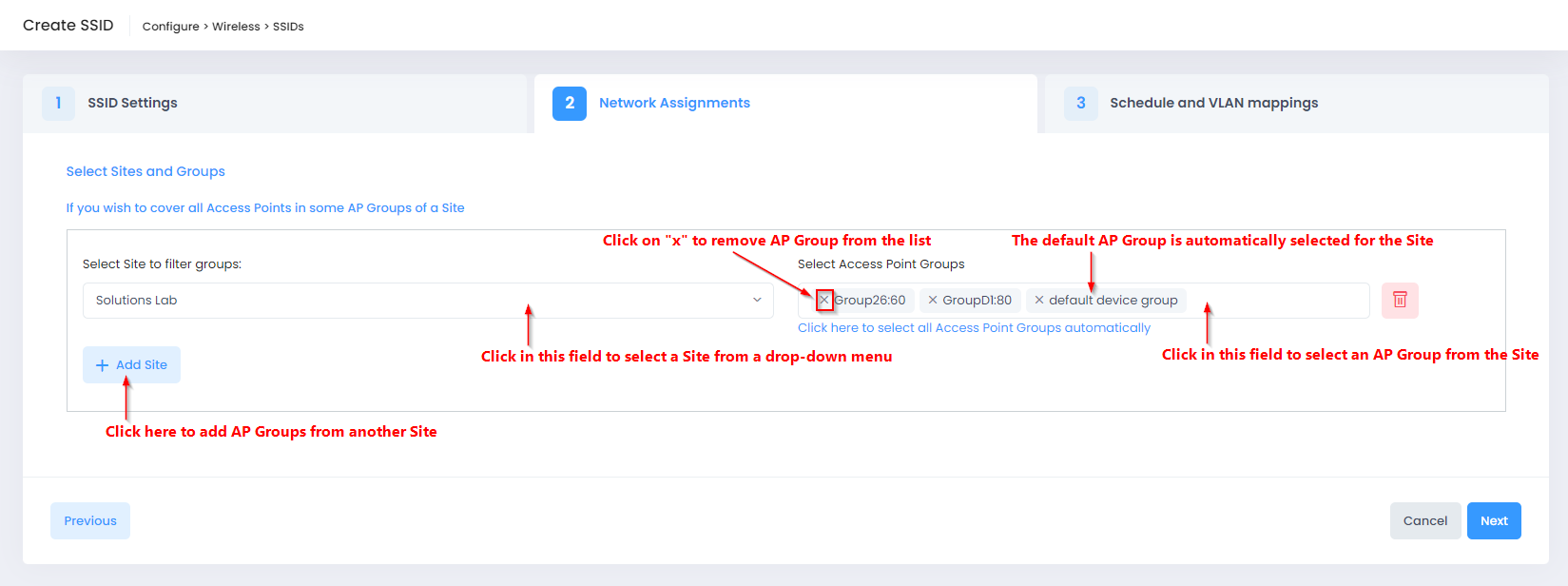
The maximum number of SSIDs per band that an AP can support is based on the AP model and whether the Extended SSID Scale option is enabled for the AP Group to which the AP belongs.
Extended SSID Scale option is disabled (the default) - AP allows a maximum of 7 SSIDs per band. This means up to 7 SSIDs with Allowed Band = 2.4GHz and up to 7 SSIDs with Allowed Band = 5GHz. If you apply an SSID to an AP Group and it causes a breach of this maximum limit, the "Save" operation will fail on that AP Group.
Extended SSID Scale option is enabled - AP models that support more than 7 SSIDs per band will allow a maximum of 14 SSIDs per band. This means up to 14 SSIDs with Allowed Band = 2.4GHz and up to 14 SSIDs with Allowed Band = 5GHz. If you apply an SSID to an AP Group and it causes a breach of this maximum limit, the "Save" operation will fail on that AP Group.
Note that the Extended SSID Scale status does not apply to 6GHz networks, which have a limit of 4 SSIDs per AP Group.
If you are editing the AP Group assignment for an SSID, all of the AP Groups to which the SSID was applied are displayed as pre-selected in the “Select Access Point Groups” field. You can then remove and/or add AP Groups, as needed.
When you are done selecting the AP Groups to apply to the SSID, click on Next to go to the Schedule and VLAN Mappings tab (Step 3).
3. Schedule and VLAN Mappings
The Schedule and VLAN Mappings tab is used to schedule the SSID availability for devices belonging to the selected AP Groups and to map a VLAN or Tunnel service to the SSID.
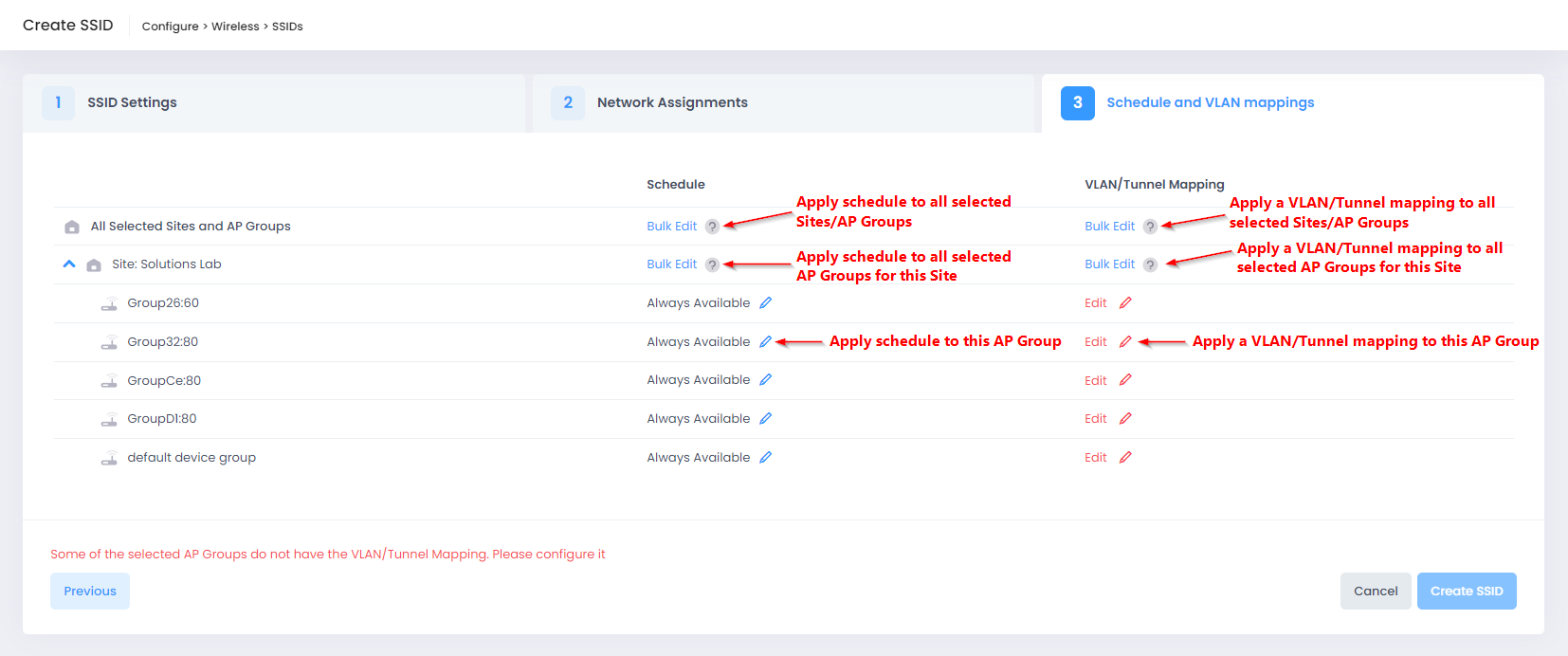
When you are done configuring the Schedule and VLAN/Tunnel mappings, click on Create SSID. The SSID profile is created.
Schedule
You can configure the SSID availability for all AP Groups across all Sites in the Organization, for all AP Groups associated with a specific Site, or for the selected AP Group.
When you click on the Bulk Edit option or the Edit option for an individual AP Group, the following Schedule Mapping screen opens:
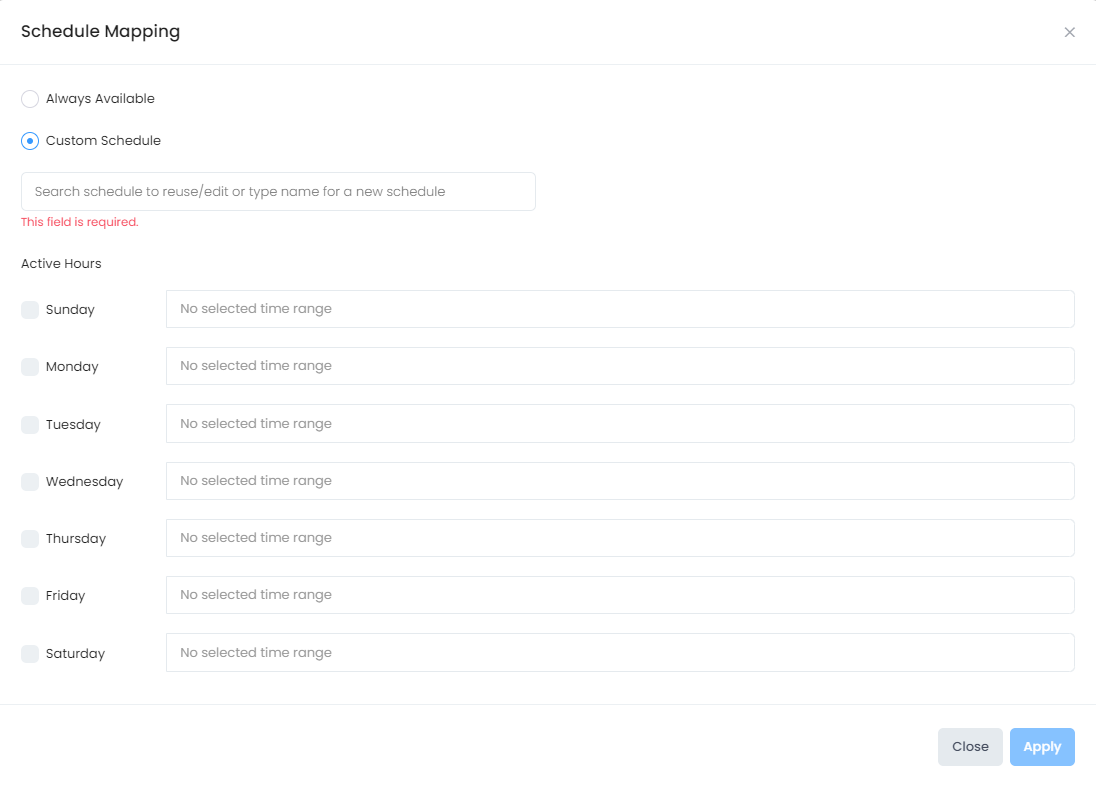
Always Available - The SSID network is available to clients 24/7.
Custom Schedule - Define specific days/times during which the SSID network is available to clients.
Active Hours - Select the days during which the SSID is active.
Select Time - When you select a specific day, you can also specify the time of day during which the SSID is active.
You can configure up to 24 time ranges for an SSID schedule, but make sure that each time range does not overlap with any other time range.
VLAN/Tunnel Mapping
You can configure a VLAN/Tunnel mapping for all AP Groups across all Sites in the Organization, for all AP Groups associated with a specific Site, or for the selected AP Group.
When you click on the Bulk Edit option or the Edit option for an individual AP Group, the following VLAN/Tunnel Mapping screen opens:
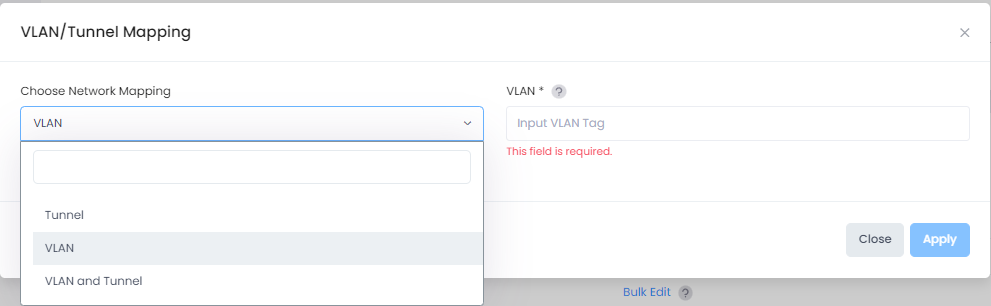
Select one of the following network mapping options from the drop-down menu:
VLAN- Maps the profile to a specific VLAN ID tag on network devices. You can enter multiple VLAN ID tags in this field by specifying a range of VLAN IDs (10-20), individual VLAN IDs (25), or both (10-20, 25). Note that after each VLAN ID entry, you must press the tab key before making the next entry. For example, enter “10-20” press tab key, then enter “21” press tab key, then enter “22” press tab key, and so on. You can also click outside of this field after each entry, instead of pressing the tab key.
Tunnel - Maps the profile to a Guest Tunnel.
VLAN and Tunnel - Maps the profile to a VLAN and a Tunnel, allowing VLAN tagging inside the Guest Tunnel.
Notes:
You cannot map the profile to VLAN 1, and the VLAN ID specified must not exceed 4090. Make sure that the VLAN ID does not overlap with other VLAN ID mappings.
The ability to bind up to 256 VLANs to a WLAN/SSID on the AP13xx/AP14xx models is supported. However, not every AP model can accommodate 256 VLANs for all the configured SSIDs. The limitations are outlined below:
AP1301H can support 256 VLANs on a maximum of 2 SSIDs, with a total of 512.
AP1311/AP1301/AP1431/AP1411 can support 256 VLANs on a maximum of 4 WLANs/SSIDs, with a total of 1024.
AP1320/AP1331/AP1351/AP1451 can accommodate 256 VLANs on a maximum of 7 WLANs/SSIDs, with a total of 1792.
When you select the Tunnel mapping option, the following fields are displayed on the VLAN/Tunnel Mapping screen:
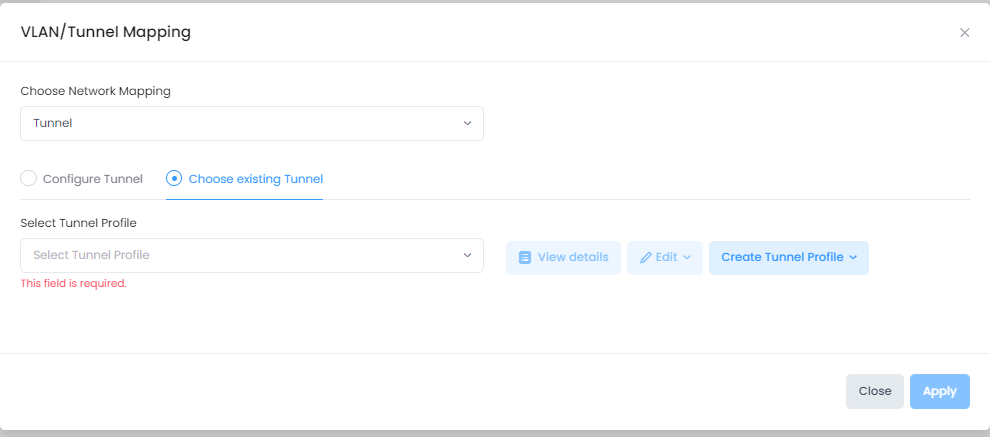
Configure Tunnel - Select this option to define a Guest Tunnel service to assign to the SSID.. When you select this option, a Tunnel Profile is automatically created with the SSID name.
Save this as a distinct Tunnel Profile, for reuse - Select this option if you want the tunnel mapping to be available for use after the associated SSID configuration has been deleted. When you click on this option, you will be prompted to enter a Tunnel Profile name.
Choose Existing Tunnel - Select an existing Guest Tunnel Profile from the drop-down menu or click on Create Tunnel Profile to open the Create Tunnel Profile screen and create a new Guest Tunnel Profile. You can also click on View Details to view information about the selected Tunnel Profile or click on Edit to open the Edit Tunnel Profile screen and make changes to the selected Tunnel Profile.